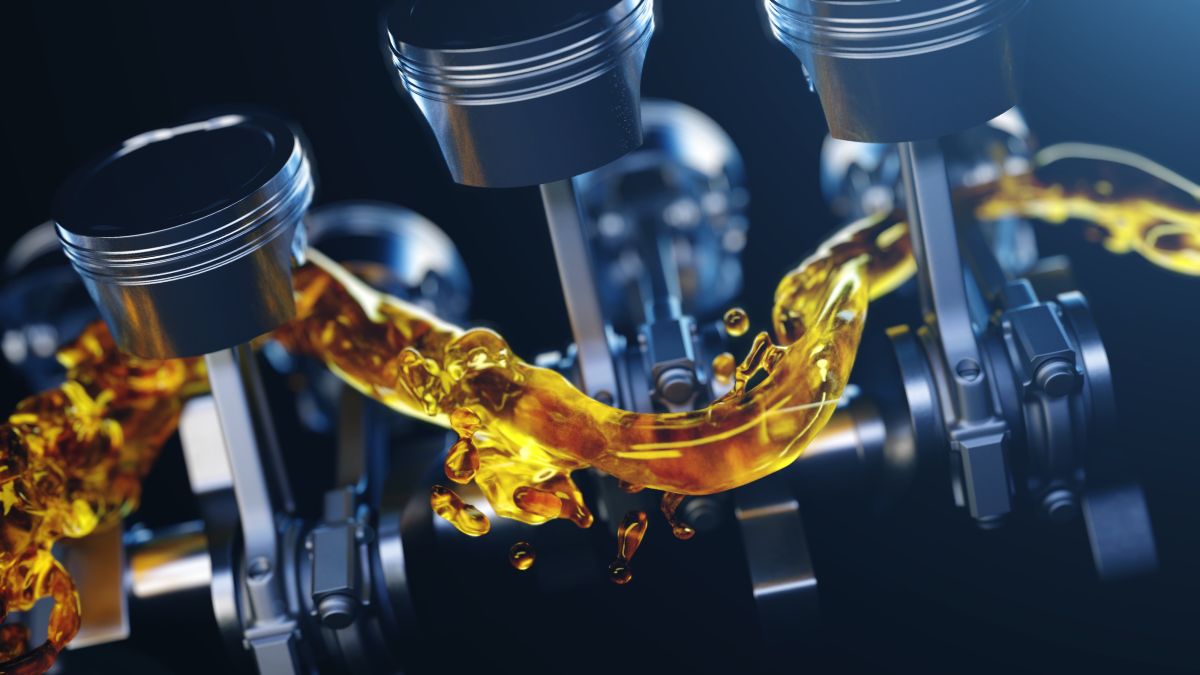
Adding or changing the oil is one of the maintenance services that most car owners perform on their own. However, there are many doubts and know what happens if you use Thickening motor oils are one of the most common.
While it is best to use what is recommended in your owner’s manual, Inadvertent use with a viscosity higher or lower than recommended is generally harmless long-term.
Engines are designed to use a certain viscosity of engine oil
Today’s advanced engines are designed to withstand much stronger than their predecessors. For example, the distances between the crankshaft magazines and the main bearings are narrower. This is done on purpose to allow modern engines to use low viscosity motor oil such as 0W-20 and even 0W-16.
Low-viscosity oils reduce internal friction because they flow more easily than high-viscosity oils, which improves fuel economy. As fuel economy standards become more stringent, automakers are turning to lower-viscosity lubricants to help them meet the requirements.
Thick oil may not flow fast enough
Not only that, but the engine will waste energy pumping out thicker oil, which reduces fuel economy. Because thick oil does not transfer heat like thin oil, operating temperatures will rise, which can lead to accelerated chemical decomposition and harmful sludge and sediment.
***
It might interest you:
How Lucas Transmission Fix Works in Your Car
3 of the best products to clean your car’s catalytic converter